Interpolation basic algorithms
It’s ineresting know how works the interpolation algorithms applied to images, in this article we are going to explore basically the most common interpolation algorithms that are: Nearest, bilinear and bicubic interpolations and their formulas.
To show the artifacts of interpolations we scaled the images to show better how to affect the interpolations
Original image:

Nearest interpolation

Bilinear interpolation

Bicubic interpolation

Nearest pixel interpolation
This is the simplest and fastest way to calculate the value of pixel. This consists in getting the nearest pixel corresponding to the original image.
If the result of inverse function get the pixel (0.3,0) then we get the value (0,0), and if we get the pixel (0.7,0) we get the value of pixel (1,0).
This is the fastest algorithm but it makes a pixeled image.
Original:

Result:

Bilinear pixel interpolation
This method of interpolation consists in tracing a line between the low and high rounded value of returned inverse function and calculate the resultant value with the line function.
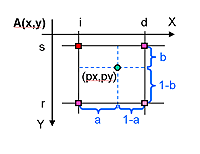
The formula:
A’(px, py) = (1-a)(1-b)A(s, i) + a(1-b)A(s, d) +(1-a)bA(r, i) + abA(r, d)
Original:

Result:

Bicubic pixel interpolation
This method produces the better result but is the slowest algorithm. It calcules the value with a cubic curve with the 4 neighbour pixels.
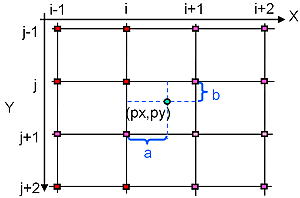
The formula:
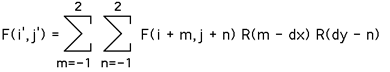
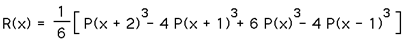
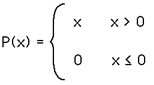
Original:

Result:
